Beach Sunset Yoga Hawaii believes in the rare benefits that comes from the original teachings of India. The Founder went to the foothills of the Himalayas in India to live for a while as gurus say its critical to to ensure authentic teachings are passed down. Thus, we offer India trained Ashtanga (8 limb original intent practice) based vinyasa flow and mindful meditation training from the home in exile of the current Dalai Lama, as well as MBSR (mindfulness based stress reduction) techniques out of academia,
Providing the practice as a moving meditation, as Yoga original intent was meant to be; not just fitness, but rather a disciplined practice of the overall wellness and cultivating control of your body, senses and mind. Contact Beach Sunset Yoga Hawaii : )
Providing the practice as a moving meditation, as Yoga original intent was meant to be; not just fitness, but rather a disciplined practice of the overall wellness and cultivating control of your body, senses and mind. Contact Beach Sunset Yoga Hawaii : )
Ashtanga Based Mindful Integrated flows
Ashtanga, being the foundation of all Vinyasas is a favorite style of athletes as well as those wanting an authentic yoga practice because it is both dynamic and yet mindful, a perfect balance of strength and ease, working on your entire body in proper chronology with every practice; synchronized movement with breath for a moving meditation, akin to the martial arts goals. Beach Sunset Yoga Hawaii classes are taught outdoors to integrate in a component of mindful connection to nature and the present moment, practicing peace with all which we cannot control. All classes taught in accordance with the speed and energy levels of the groups that attend; were trained and highly experienced in mixed level classes so that all can feel engaged, from 1st timer to advance.
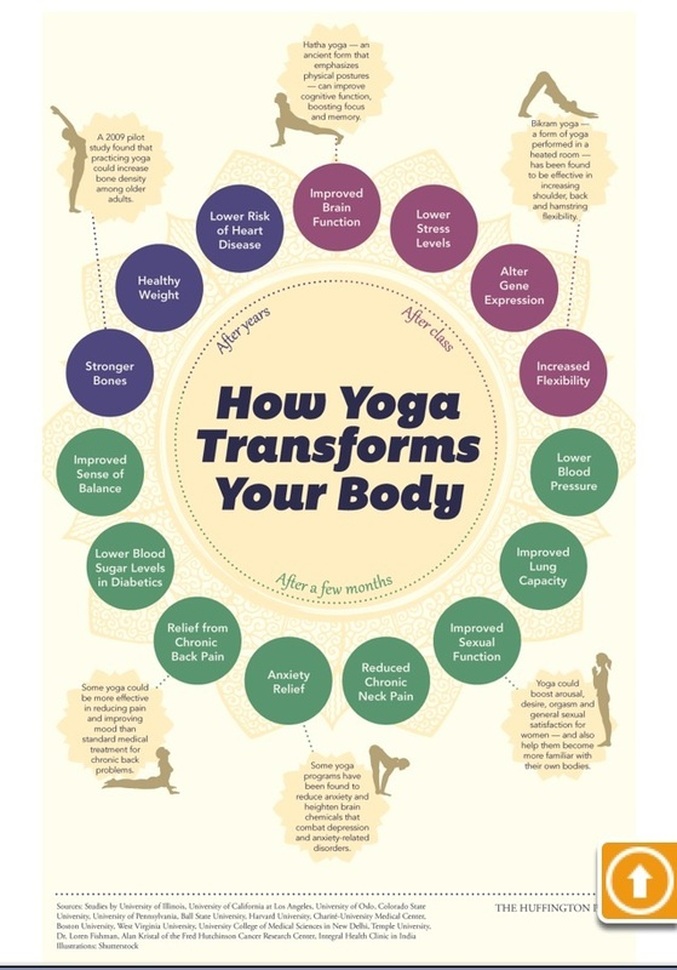
See Benefits of Yoga and Ashtanga here.
Beach Sunset Yoga Hawaii has trained in feedback sessions with doctors from Orthopedic clinics, University of Hawaii, Firefighters, Golfers, and Surfers.
KEEPING YOGA REAL
India trained ashtanga based vinyasa flow is an authentic mindful practice for comprehensive wellness of mind and body. We adhere to modern medicines support of a practice of optimum physical health. We honor anciently documented techniques and philosophies for calmness and equanimity within oneself. Through your breath, once fluently practiced, control of vast physical, emotional and mental reactions come second nature.
India trained ashtanga based vinyasa flow is an authentic mindful practice for comprehensive wellness of mind and body. We adhere to modern medicines support of a practice of optimum physical health. We honor anciently documented techniques and philosophies for calmness and equanimity within oneself. Through your breath, once fluently practiced, control of vast physical, emotional and mental reactions come second nature.
YOGAS BENEFITS ARE UNIQUE
The benefits of yoga on our physical health are well documented by eastern as well as western medicine. But yoga is not just about postures, its the only physical exercise program that works on the inter-connectedness of your mind, body and actions; and even spirit if you wish. We aim to transfer and sustain the original teachings of these time proven methods and philosophies of a life of substance as dictated by the other 7 branches of Ashtanga's complete yoga practice.
Yoga aims for the balance between strength and flexibility for control, ease of pain and range of motion.
This is why its so important for us to help sustain what was passed onto us in India, to help build comprehensive health; and encourage its unique practice of aiming for greater consciousness purity and compassion through a very mindful practice.
Practice an anciently and medically modern supported routine that comprehensively works to ease every muscle of your body, strengthens your bones, releases endorphin, and increase your body's entire internal wellness.
The benefits of yoga on our physical health are well documented by eastern as well as western medicine. But yoga is not just about postures, its the only physical exercise program that works on the inter-connectedness of your mind, body and actions; and even spirit if you wish. We aim to transfer and sustain the original teachings of these time proven methods and philosophies of a life of substance as dictated by the other 7 branches of Ashtanga's complete yoga practice.
Yoga aims for the balance between strength and flexibility for control, ease of pain and range of motion.
This is why its so important for us to help sustain what was passed onto us in India, to help build comprehensive health; and encourage its unique practice of aiming for greater consciousness purity and compassion through a very mindful practice.
Practice an anciently and medically modern supported routine that comprehensively works to ease every muscle of your body, strengthens your bones, releases endorphin, and increase your body's entire internal wellness.
Why Ashtanga. We want to help transfer the original teachings from India, to sustain it for our posterity into the future of our modern world. As we see often times yoga's teachings in the west being watered down in biologically unhealthy ways and away from the original philosophies of substance, we focus our teachings on the ancient tested methods that have resulted in peoples unbelievably beneficial results physically and mentally for thousands of years, with even reports of this series work in correcting scoliosis.
We maintain that proper alignment, blood circulation, and the yoga breathe; the underscoring of longevity of holistic wellness over competition, image and even flexibility; practiced in its synchronized proper sequence of breath and movements, as well as a mental dedication to greater consciousness and depth, compassion and mindfulness, with or without spirituality; is what has changed peoples health, attitudes, lifestyles and all around lives towards being more positive, internally healthy, pure, freeing, centered able-bodied people, much less susceptible to disease and emotional turmoil; with the channeling of energys flow through breath and focus, providing for greater mental and physical strength and stability and overall mind/body awareness. Ashtanga brings back the origins of mindfulness and substance that people find lacking in westernized power gym - corporate type yoga.
The flow style is not a constant as in modern styled power yoga, but rather takes advantage of the ebb and flow of energy for optimization of focus; switching between the flow of vinyasas and holding postures for muscle resistance benefits as derived in Ashtanga. The sequence of Ashtanga postures in its chronology is the one renowned for its historically demonstrated optimum health benefits.
Ashtanga yoga is a favorite among athletes and those active; it is the base of of the Vinyasa style, increasingly becoming the most popular style overall as it provides for a blend of fluidity and strength, turning static asanas into dynamic flows that provide consistency in working on all your muscle groups and proper alignment. Ashtanga's fluidity and synchronization with breath in movements allows for yoga to be what it was intended and what uniquely allows for it to be, a meditative process, which among many other benefits, has shown to decrease the risk of heart attacks and overcoming mental challenges.
We maintain that proper alignment, blood circulation, and the yoga breathe; the underscoring of longevity of holistic wellness over competition, image and even flexibility; practiced in its synchronized proper sequence of breath and movements, as well as a mental dedication to greater consciousness and depth, compassion and mindfulness, with or without spirituality; is what has changed peoples health, attitudes, lifestyles and all around lives towards being more positive, internally healthy, pure, freeing, centered able-bodied people, much less susceptible to disease and emotional turmoil; with the channeling of energys flow through breath and focus, providing for greater mental and physical strength and stability and overall mind/body awareness. Ashtanga brings back the origins of mindfulness and substance that people find lacking in westernized power gym - corporate type yoga.
The flow style is not a constant as in modern styled power yoga, but rather takes advantage of the ebb and flow of energy for optimization of focus; switching between the flow of vinyasas and holding postures for muscle resistance benefits as derived in Ashtanga. The sequence of Ashtanga postures in its chronology is the one renowned for its historically demonstrated optimum health benefits.
Ashtanga yoga is a favorite among athletes and those active; it is the base of of the Vinyasa style, increasingly becoming the most popular style overall as it provides for a blend of fluidity and strength, turning static asanas into dynamic flows that provide consistency in working on all your muscle groups and proper alignment. Ashtanga's fluidity and synchronization with breath in movements allows for yoga to be what it was intended and what uniquely allows for it to be, a meditative process, which among many other benefits, has shown to decrease the risk of heart attacks and overcoming mental challenges.
Ashtanga provides the base for an authentic practice of comprehensive mind and body ease; the balance of strength through energy control and agility. It is the consistent flow of breath that provides for a moving meditation as originally intended for yoga.
It is a type of yoga that works in chronological
steps throughout your muscle, joints and organs, in every session, like the way oiling a car works for its engine; its use of disciplined energy and non focus on end fancy posture holds true to the non attachment goal in its philosophy; and its linking of breath even in transitions and holds between flows, and its simplicity and clarity in instructions, is what makes for the mindful practice.
It is a type of yoga that works in chronological
steps throughout your muscle, joints and organs, in every session, like the way oiling a car works for its engine; its use of disciplined energy and non focus on end fancy posture holds true to the non attachment goal in its philosophy; and its linking of breath even in transitions and holds between flows, and its simplicity and clarity in instructions, is what makes for the mindful practice.
More then just postures : 8 limbs of Yoga
Ashtanga is the yoga of Patangali, the creator of the original Yoga Sutras, and developer of the 8 limb structure of yoga. We aim to transfer and sustain the original teachings of these time proven methods and philosophies of a compassionate living of substance as dictated by the other 7 branches of Ashtanga's true yoga practice . We adhere to these principals not primarily for their customs nor history, but rather for their values and centuries old demonstrated results so unique to yoga.
Ashtanga is the yoga of Patangali, the creator of the original Yoga Sutras, and developer of the 8 limb structure of yoga. We aim to transfer and sustain the original teachings of these time proven methods and philosophies of a compassionate living of substance as dictated by the other 7 branches of Ashtanga's true yoga practice . We adhere to these principals not primarily for their customs nor history, but rather for their values and centuries old demonstrated results so unique to yoga.
38 Ways Yoga Keeps You Fit By Timothy McCall, M.D.
If you're a passionate yoga practitioner, you've probably noticed the ways yoga works—maybe you're sleeping better or getting fewer colds or just feeling more relaxed and at ease. But if you've ever tried telling a newbie how it works, you might find that explanations like "It increases the flow of prana" or "It brings energy up your spine" fall on deaf or skeptical ears.
As it happens, Western science is starting to provide some concrete clues as to how yoga works to improve health, heal aches and pains, and keep sickness at bay. Once you understand them, you'll have even more motivation to step onto your mat, and you probably won't feel so tongue-tied the next time someone wants Western proof.
I myself have experienced yoga's healing power in a very real way. Weeks before a trip to India in 2002 to investigate yoga therapy, I developed numbness and tingling in my right hand. After first considering scary things like a brain tumor and multiple sclerosis, I figured out that the cause of the symptoms was thoracic outlet syndrome, a nerve blockage in my neck and chest.
Despite the uncomfortable symptoms, I realized how useful my condition could be during my trip. While visiting various yoga therapy centers, I would submit myself for evaluation and treatment by the various experts I'd arranged to observe. I could try their suggestions and see what worked for me. While this wasn't exactly a controlled scientific experiment, I knew that such hands-on learning could teach me things I might not otherwise understand.
My experiment proved illuminating. At the Vivekananda ashram just outside of Bangalore, S. Nagarathna, M.D., recommended breathing exercises in which I imagined bringing prana (vital energy) into my right upper chest. Other therapy included asana, pPranayama, meditation, chanting, lectures on philosophy, and various kriya (internal cleansing practices). At the Krishnamacharya Yoga Mandiram in Chennai and from A.G. Mohan and his wife, Indra, who practice just outside of Chennai, I was told to stop practicing Headstand and Shoulderstand in favor of gentle asana coordinated with the breath. In Pune, S.V. Karandikar, a medical doctor, recommended practices with ropes and belts to put traction on my spine and exercises that taught me to use my shoulder blades to open my upper back.
Thanks to the techniques I learned in India, advice from teachers in the United States, and my own exploration, my chest is more flexible than it was, my posture has improved, and for more than a year, I've been free of symptoms.
My experience inspired me to pore over the scientific studies I'd collected in India as well as the West to identify and explain how yoga can both prevent disease and help you recover from it. Here is what I found.
Flex Time
1 Improved flexibility is one of the first and most obvious benefits of yoga. During your first class, you probably won't be able to touch your toes, never mind do a backbend. But if you stick with it, you'll notice a gradual loosening, and eventually, seemingly impossible poses will become possible. You'll also probably notice that aches and pains start to disappear. That's no coincidence. Tight hips can strain the knee joint due to improper alignment of the thigh and shinbones. Tight hamstrings can lead to a flattening of the lumbar spine, which can cause back pain. And inflexibility in muscles and connective tissue, such as fascia and ligaments, can cause poor posture.
Strength Test
2 Strong muscles do more than look good. They also protect us from conditions like arthritis and back pain, and help prevent falls in elderly people. And when you build strength through yoga, you balance it with flexibility. If you just went to the gym and lifted weights, you might build strength at the expense of flexibility.
Standing Orders
3 Your head is like a bowling ball—big, round, and heavy. When it's balanced directly over an erect spine, it takes much less work for your neck and back muscles to support it. Move it several inches forward, however, and you start to strain those muscles. Hold up that forward-leaning bowling ball for eight or 12 hours a day and it's no wonder you're tired. And fatigue might not be your only problem. Poor posture can cause back, neck, and other muscle and joint problems. As you slump, your body may compensate by flattening the normal inward curves in your neck and lower back. This can cause pain and degenerative arthritis of the spine.
Joint Account
4 Each time you practice yoga, you take your joints through their full range of motion. This can help prevent degenerative arthritis or mitigate disability by "squeezing and soaking" areas of cartilage that normally aren't used. Joint cartilage is like a sponge; it receives fresh nutrients only when its fluid is squeezed out and a new supply can be soaked up. Without proper sustenance, neglected areas of cartilage can eventually wear out, exposing the underlying bone like worn-out brake pads.
Spinal Rap
5 Spinal disks—the shock absorbers between the vertebrae that can herniate and compress nerves—crave movement. That's the only way they get their nutrients. If you've got a well-balanced asana practice with plenty of backbends, forward bends, and twists, you'll help keep your disks supple.
Bone Zone
6It's well documented that weight-bearing exercise strengthens bones and helps ward off osteoporosis. Many postures in yoga require that you lift your own weight. And some, like Downward- and Upward-Facing Dog, help strengthen the arm bones, which are particularly vulnerable to osteoporotic fractures. In an unpublished study conducted at California State University, Los Angeles, yoga practice increased bone density in the vertebrae. Yoga's ability to lower levels of the stress hormone cortisol (see Number 11) may help keep calcium in the bones.
Flow Chart
7 Yoga gets your blood flowing. More specifically, the relaxation exercises you learn in yoga can help your circulation, especially in your hands and feet. Yoga also gets more oxygen to your cells, which function better as a result. Twisting poses are thought to wring out venous blood from internal organs and allow oxygenated blood to flow in once the twist is released. Inverted poses, such as Headstand, Handstand, and Shoulderstand, encourage venous blood from the legs and pelvis to flow back to the heart, where it can be pumped to the lungs to be freshly oxygenated. This can help if you have swelling in your legs from heart or kidney problems. Yoga also boosts levels of hemoglobin and red blood cells, which carry oxygen to the tissues. And it thins the blood by making platelets less sticky and by cutting the level of clot-promoting proteins in the blood. This can lead to a decrease in heart attacks and strokes since blood clots are often the cause of these killers.
Lymph Lesson
8 When you contract and stretch muscles, move organs around, and come in and out of yoga postures, you increase the drainage of lymph (a viscous fluid rich in immune cells). This helps the lymphatic system fight infection, destroy cancerous cells, and dispose of the toxic waste products of cellular functioning.
Heart Start
9 When you regularly get your heart rate into the aerobic range, you lower your risk of heart attack and can relieve depression. While not all yoga is aerobic, if you do it vigorously or take flow or Ashtanga classes, it can boost your heart rate into the aerobic range. But even yoga exercises that don't get your heart rate up that high can improve cardiovascular conditioning. Studies have found that yoga practice lowers the resting heart rate, increases endurance, and can improve your maximum uptake of oxygen during exercise—all reflections of improved aerobic conditioning. One study found that subjects who were taught only pranayama could do more exercise with less oxygen.
Pressure Drop
10 If you've got high blood pressure, you might benefit from yoga. Two studies of people with hypertension, published in the British medical journal The Lancet, compared the effects of Savasana (Corpse Pose) with simply lying on a couch. After three months, Savasana was associated with a 26-point drop in systolic blood pressure (the top number) and a 15-point drop in diastolic blood pressure (the bottom number—and the higher the initial blood pressure, the bigger the drop.
Worry Thwarts
11 Yoga lowers cortisol levels. If that doesn't sound like much, consider this. Normally, the adrenal glands secrete cortisol in response to an acute crisis, which temporarily boosts immune function. If your cortisol levels stay high even after the crisis, they can compromise the immune system. Temporary boosts of cortisol help with long-term memory, but chronically high levels undermine memory and may lead to permanent changes in the brain. Additionally, excessive cortisol has been linked with major depression, osteoporosis (it extracts calcium and other minerals from bones and interferes with the laying down of new bone), high blood pressure, and insulin resistance. In rats, high cortisol levels lead to what researchers call "food-seeking behavior" (the kind that drives you to eat when you're upset, angry, or stressed). The body takes those extra calories and distributes them as fat in the abdomen, contributing to weight gain and the risk of diabetes and heart attack.
Happy Hour
12 Feeling sad? Sit in Lotus. Better yet, rise up into a backbend or soar royally into King Dancer Pose. While it's not as simple as that, one study found that a consistent yoga practice improved depression and led to a significant increase in serotonin levels and a decrease in the levels of monoamine oxidase (an enzyme that breaks down neurotransmitters) and cortisol. At the University of Wisconsin, Richard Davidson, Ph.D., found that the left prefrontal cortex showed heightened activity in meditators, a finding that has been correlated with greater levels of happiness and better immune function. More dramatic left-sided activation was found in dedicated, long-term practitioners.
Weighty Matters
13 Move more, eat less—that's the adage of many a dieter. Yoga can help on both fronts. A regular practice gets you moving and burns calories, and the spiritual and emotional dimensions of your practice may encourage you to address any eating and weight problems on a deeper level. Yoga may also inspire you to become a more conscious eater.
Low Show
14 Yoga lowers blood sugar and LDL ("bad") cholesterol and boosts HDL ("good") cholesterol. In people with diabetes, yoga has been found to lower blood sugar in several ways: by lowering cortisol and adrenaline levels, encouraging weight loss, and improving sensitivity to the effects of insulin. Get your blood sugar levels down, and you decrease your risk of diabetic complications such as heart attack, kidney failure, and blindness.
Brain Waves
15 An important component of yoga is focusing on the present. Studies have found that regularyoga practice improves coordination, reaction time, memory, and even IQ scores. People who practice Transcendental Meditation demonstrate the ability to solve problems and acquire and recall information better—probably because they're less distracted by their thoughts, which can play over and over like an endless tape loop.
Nerve Center
16 Yoga encourages you to relax, slow your breath, and focus on the present, shifting the balance from the sympathetic nervous system (or the fight-or-flight response) to the parasympathetic nervous system. The latter is calming and restorative; it lowers breathing and heart rates, decreases blood pressure, and increases blood flow to the intestines and reproductive organs—comprising what Herbert Benson, M.D., calls the relaxation response.
Space Place
17 Regularly practicing yoga increases proprioception (the ability to feel what your body is doing and where it is in space) and improves balance. People with bad posture or dysfunctional movement patterns usually have poor proprioception, which has been linked to knee problems and back pain. Better balance could mean fewer falls. For the elderly, this translates into more independence and delayed admission to a nursing home or never entering one at all. For the rest of us, postures like Tree Pose can make us feel less wobbly on and off the mat.
Control Center
18 Some advanced yogis can control their bodies in extraordinary ways, many of which are mediated by the nervous system. Scientists have monitored yogis who could induce unusual heart rhythms, generate specific brain-wave patterns, and, using a meditation technique, raise the temperature of their hands by 15 degrees Fahrenheit. If they can use yoga to do that, perhaps you could learn to improve blood flow to your pelvis if you're trying to get pregnant or induce relaxation when you're having trouble falling asleep.
Loose Limbs
19 Do you ever notice yourself holding the telephone or a steering wheel with a death grip or scrunching your face when staring at a computer screen? These unconscious habits can lead to chronic tension, muscle fatigue, and soreness in the wrists, arms, shoulders, neck, and face, which can increase stress and worsen your mood. As you practice yoga, you begin to notice where you hold tension: It might be in your tongue, your eyes, or the muscles of your face and neck. If you simply tune in, you may be able to release some tension in the tongue and eyes. With bigger muscles like the quadriceps, trapezius, and buttocks, it may take years of practice to learn how to relax them.
Chill Pill
20 Stimulation is good, but too much of it taxes the nervous system. Yoga can provide relief from the hustle and bustle of modern life. Restorative asana, yoga nidra (a form of guided relaxation), Savasana, pranayama, and meditation encourage pratyahara, a turning inward of the senses, which provides downtime for the nervous system. Another by-product of a regular yoga practice, studies suggest, is better sleep—which means you'll be less tired and stressed and less likely to have accidents.
Immune Boon
21 Asana and pranayama probably improve immune function, but, so far, meditation has the strongest scientific support in this area. It appears to have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the immune system, boosting it when needed (for example, raising antibody levels in response to a vaccine) and lowering it when needed (for instance, mitigating an inappropriately aggressive immune function in an autoimmune disease like psoriasis).
Breathing Room
22 Yogis tend to take fewer breaths of greater volume, which is both calming and more efficient. A 1998 study published in The Lancet taught a yogic technique known as "complete breathing" to people with lung problems due to congestive heart failure. After one month, their average respiratory rate decreased from 13.4 breaths per minute to 7.6. Meanwhile, their exercise capacity increased significantly, as did the oxygen saturation of their blood. In addition, yoga has been shown to improve various measures of lung function, including the maximum volume of the breath and the efficiency of the exhalation.
Yoga also promotes breathing through the nose, which filters the air, warms it (cold, dry air is more likely to trigger an asthma attack in people who are sensitive), and humidifies it, removing pollen and dirt and other things you'd rather not take into your lungs.
Poop Scoop
23 Ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, constipation—all of these can be exacerbated by stress. So if you stress less, you'll suffer less. Yoga, like any physical exercise, can ease constipation—and theoretically lower the risk of colon cancer—because moving the body facilitates more rapid transport of food and waste products through the bowels. And, although it has not been studied scientifically, yogis suspect that twisting poses may be beneficial in getting waste to move through the system.
Peace of Mind
24 Yoga quells the fluctuations of the mind, according to Patanjali's Yoga Sutra. In other words, it slows down the mental loops of frustration, regret, anger, fear, and desire that can cause stress. And since stress is implicated in so many health problems—from migraines and insomnia to lupus, MS, eczema, high blood pressure, and heart attacks—if you learn to quiet your mind, you'll be likely to live longer and healthier.
Divine Sign
25 Many of us suffer from chronic low self-esteem. If you handle this negatively—take drugs, overeat, work too hard, sleep around—you may pay the price in poorer health physically, mentally, and spiritually. If you take a positive approach and practice yoga, you'll sense, initially in brief glimpses and later in more sustained views, that you're worthwhile or, as yogic philosophy teaches, that you are a manifestation of the Divine. If you practice regularly with an intention of self-examination and betterment—not just as a substitute for an aerobics class—you can access a different side of yourself. You'll experience feelings of gratitude, empathy, and forgiveness, as well as a sense that you're part of something bigger. While better health is not the goal of spirituality, it's often a by-product, as documented by repeated scientific studies.
Pain Drain
26 Yoga can ease your pain. According to several studies, asana, meditation, or a combination of the two, reduced pain in people with arthritis, back pain, fibromyalgia, carpal tunnel syndrome, and other chronic conditions. When you relieve your pain, your mood improves, you're more inclined to be active, and you don't need as much medication.
Heat Treatment
27 Yoga can help you make changes in your life. In fact, that might be its greatest strength. Tapas, the Sanskrit word for "heat," is the fire, the discipline that fuels yoga practice and that regular practice builds. The tapas you develop can be extended to the rest of your life to overcome inertia and change dysfunctional habits. You may find that without making a particular effort to change things, you start to eat better, exercise more, or finally quit smoking after years of failed attempts.
Guru Gifts
28 Good yoga teachers can do wonders for your health. Exceptional ones do more than guide you through the postures. They can adjust your posture, gauge when you should go deeper in poses or back off, deliver hard truths with compassion, help you relax, and enhance and personalize your practice. A respectful relationship with a teacher goes a long way toward promoting your health.
Drug Free
29 If your medicine cabinet looks like a pharmacy, maybe it's time to try yoga. Studies of people with asthma, high blood pressure, Type II diabetes (formerly called adult-onset diabetes), and obsessive-compulsive disorder have shown that yoga helped them lower their dosage of medications and sometimes get off them entirely. The benefits of taking fewer drugs? You'll spend less money, and you're less likely to suffer side effects and risk dangerous drug interactions.
Hostile Makeover
30 Yoga and meditation build awareness. And the more aware you are, the easier it is to break free of destructive emotions like anger. Studies suggest that chronic anger and hostility are as strongly linked to heart attacks as are smoking, diabetes, and elevated cholesterol. Yoga appears to reduce anger by increasing feelings of compassion and interconnection and by calming the nervous system and the mind. It also increases your ability to step back from the drama of your own life, to remain steady in the face of bad news or unsettling events. You can still react quickly when you need to—and there's evidence that yoga speeds reaction time—but you can take that split second to choose a more thoughtful approach, reducing suffering for yourself and others.
Good Relations
31 Love may not conquer all, but it certainly can aid in healing. Cultivating the emotional support of friends, family, and community has been demonstrated repeatedly to improve health and healing. A regular yoga practice helps develop friendliness, compassion, and greater equanimity. Along with yogic philosophy's emphasis on avoiding harm to others, telling the truth, and taking only what you need, this may improve many of your relationships.
Sound System
32 The basics of yoga—asana, pranayama, and meditation—all work to improve your health, but there's more in the yoga toolbox. Consider chanting. It tends to prolong exhalation, which shifts the balance toward the parasympathetic nervous system. When done in a group, chanting can be a particularly powerful physical and emotional experience. A recent study from Sweden's Karolinska Institute suggests that humming sounds—like those made while chanting Om—open the sinuses and facilitate drainage.
Vision Quest
33 If you contemplate an image in your mind's eye, as you do in yoga nidra and other practices, you can effect change in your body. Several studies have found that guided imagery reduced postoperative pain, decreased the frequency of headaches, and improved the quality of life for people with cancer and HIV.
Clean Machine
34 Kriyas, or cleansing practices, are another element of yoga. They include everything from rapid breathing exercises to elaborate internal cleansings of the intestines. Jala neti, which entails a gentle lavage of the nasal passages with salt water, removes pollen and viruses from the nose, keeps mucus from building up, and helps drains the sinuses.
Karma Concept
35 Karma yoga (service to others) is integral to yogic philosophy. And while you may not be inclined to serve others, your health might improve if you do. A study at the University of Michigan found that older people who volunteered a little less than an hour per week were three times as likely to be alive seven years later. Serving others can give meaning to your life, and your problems may not seem so daunting when you see what other people are dealing with.
Healing Hope
36 In much of conventional medicine, most patients are passive recipients of care. In yoga, it's what you do for yourself that matters. Yoga gives you the tools to help you change, and you might start to feel better the first time you try practicing. You may also notice that the more you commit to practice, the more you benefit. This results in three things: You get involved in your own care, you discover that your involvement gives you the power to effect change, and seeing that you can effect change gives you hope. And hope itself can be healing.
Connective Tissue
37 As you read all the ways yoga improves your health, you probably noticed a lot of overlap. That's because they're intensely interwoven. Change your posture and you change the way you breathe. Change your breathing and you change your nervous system. This is one of the great lessons of yoga: Everything is connected—your hipbone to your anklebone, you to your community, your community to the world. This interconnection is vital to understanding yoga. This holistic system simultaneously taps into many mechanisms that have additive and even multiplicative effects. This synergy may be the most important way of all that yoga heals.
Placebo Power
38 Just believing you will get better can make you better. Unfortunately, many conventional scientists believe that if something works by eliciting the placebo effect, it doesn't count. But most patients just want to get better, so if chanting a mantra—like you might do at the beginning or end of yoga class or throughout a meditation or in the course of your day—facilitates healing, even if it's just a placebo effect, why not do it?
harvard article on breathing
Adapted from Stress Management: Approaches for preventing and reducing stress.
Proper breathing goes by many names. You may have heard it called diaphragmatic breathing, abdominal breathing, or belly breathing. When you breathe deeply, the air coming in through your nose fully fills your lungs, and you will notice that your lower belly rises. The ability to breathe so deeply and powerfully is not limited to a select few. This skill is inborn but often lies dormant. Reawakening it allows you to tap one of your body’s strongest self-healing mechanisms.
Why does breathing deeply seem unnatural to many of us? One reason may be that our culture often rewards us for stifling strong emotions. Girls and women are expected to rein in anger. Boys and men are exhorted not to cry. What happens when you hold back tears, stifle anger during a charged confrontation, tiptoe through a fearful situation, or try to keep pain at bay? Unconsciously, you hold your breath or breathe irregularly.
Body image affects breathing, too. A “washboard” stomach considered so attractive in our culture encourages men and women to constrict their stomach muscles. This adds to tension and anxiety, and gradually makes shallow “chest breathing” feel normal.
The act of breathing engages the diaphragm, a strong sheet of muscle that divides the chest from the abdomen. As you breathe in, the diaphragm drops downward, pulling your lungs with it and pressing against abdominal organs to make room for your lungs to expand as they fill with air. As you breathe out, the diaphragm presses back upward against your lungs, helping to expel carbon dioxide (see figure).
Shallow breathing hobbles the diaphragm’s range of motion. The lowest portion of the lungs — which is where many small blood vessels instrumental in carrying oxygen to cells reside — never gets a full share of oxygenated air. That can make you feel short of breath and anxious.
Deep abdominal breathing encourages full oxygen exchange — that is, the beneficial trade of incoming oxygen for outgoing carbon dioxide. Not surprisingly, this type of breathing slows the heartbeat and can lower or stabilize blood pressure.
Here’s how to take a deep, healing, diaphragmatic breath:
First steps. Find a comfortable, quiet place to sit or lie down. Start by observing your breath. First take a normal breath. Now try taking a slow, deep breath. The air coming in through your nose should move downward into your lower belly. Let your abdomen expand fully. Now breathe out through your mouth (or your nose, if that feels more natural). Alternate normal and deep breaths several times. Pay attention to how you feel when you inhale and exhale normally and when you breathe deeply. Shallow breathing often feels tense and constricted, while deep breathing produces relaxation.
Now practice diaphragmatic breathing for several minutes. Put one hand on your abdomen, just below your belly button. Feel your hand rise about an inch each time you inhale and fall about an inch each time you exhale. Your chest will rise slightly, too, in concert with your abdomen. Remember to relax your belly so that each inhalation expands it fully.
Breath focus in practice. Once you’ve taken the steps above, you can move on to regular practice of breath focus. As you sit comfortably with your eyes closed, blend your breathing with helpful imagery and a focus word or phrase that will help you relax. Imagine that the air you breathe in washes peace and calm into your body. As you breathe out, imagine that the air leaving your body carries tension and anxiety away with it. As you inhale, try saying this phrase to yourself: “Breathing in peace and calm.” And as you exhale, say: “Breathing out tension and anxiety.” When you first start, 10 minutes of breath focus is a reasonable goal. Gradually add time until your sessions are about 15 to 20 minutes long.
Proper breathing goes by many names. You may have heard it called diaphragmatic breathing, abdominal breathing, or belly breathing. When you breathe deeply, the air coming in through your nose fully fills your lungs, and you will notice that your lower belly rises. The ability to breathe so deeply and powerfully is not limited to a select few. This skill is inborn but often lies dormant. Reawakening it allows you to tap one of your body’s strongest self-healing mechanisms.
Why does breathing deeply seem unnatural to many of us? One reason may be that our culture often rewards us for stifling strong emotions. Girls and women are expected to rein in anger. Boys and men are exhorted not to cry. What happens when you hold back tears, stifle anger during a charged confrontation, tiptoe through a fearful situation, or try to keep pain at bay? Unconsciously, you hold your breath or breathe irregularly.
Body image affects breathing, too. A “washboard” stomach considered so attractive in our culture encourages men and women to constrict their stomach muscles. This adds to tension and anxiety, and gradually makes shallow “chest breathing” feel normal.
The act of breathing engages the diaphragm, a strong sheet of muscle that divides the chest from the abdomen. As you breathe in, the diaphragm drops downward, pulling your lungs with it and pressing against abdominal organs to make room for your lungs to expand as they fill with air. As you breathe out, the diaphragm presses back upward against your lungs, helping to expel carbon dioxide (see figure).
Shallow breathing hobbles the diaphragm’s range of motion. The lowest portion of the lungs — which is where many small blood vessels instrumental in carrying oxygen to cells reside — never gets a full share of oxygenated air. That can make you feel short of breath and anxious.
Deep abdominal breathing encourages full oxygen exchange — that is, the beneficial trade of incoming oxygen for outgoing carbon dioxide. Not surprisingly, this type of breathing slows the heartbeat and can lower or stabilize blood pressure.
Here’s how to take a deep, healing, diaphragmatic breath:
First steps. Find a comfortable, quiet place to sit or lie down. Start by observing your breath. First take a normal breath. Now try taking a slow, deep breath. The air coming in through your nose should move downward into your lower belly. Let your abdomen expand fully. Now breathe out through your mouth (or your nose, if that feels more natural). Alternate normal and deep breaths several times. Pay attention to how you feel when you inhale and exhale normally and when you breathe deeply. Shallow breathing often feels tense and constricted, while deep breathing produces relaxation.
Now practice diaphragmatic breathing for several minutes. Put one hand on your abdomen, just below your belly button. Feel your hand rise about an inch each time you inhale and fall about an inch each time you exhale. Your chest will rise slightly, too, in concert with your abdomen. Remember to relax your belly so that each inhalation expands it fully.
Breath focus in practice. Once you’ve taken the steps above, you can move on to regular practice of breath focus. As you sit comfortably with your eyes closed, blend your breathing with helpful imagery and a focus word or phrase that will help you relax. Imagine that the air you breathe in washes peace and calm into your body. As you breathe out, imagine that the air leaving your body carries tension and anxiety away with it. As you inhale, try saying this phrase to yourself: “Breathing in peace and calm.” And as you exhale, say: “Breathing out tension and anxiety.” When you first start, 10 minutes of breath focus is a reasonable goal. Gradually add time until your sessions are about 15 to 20 minutes long.